 There’s tons of talk about how using solar energy reduces your carbon footprint, but how exactly does it do that? Here, we’ll go over the facts of how swapping to solar energy drastically reduces your household’s carbon emissions. From the manufacturing of solar panels to energy production and even disposal, solar energy is the greener choice for homeowners and businesses.
There’s tons of talk about how using solar energy reduces your carbon footprint, but how exactly does it do that? Here, we’ll go over the facts of how swapping to solar energy drastically reduces your household’s carbon emissions. From the manufacturing of solar panels to energy production and even disposal, solar energy is the greener choice for homeowners and businesses.
Manufacturing Solar Panels Is Less Harmful To The Environment Than Extracting Fossil Fuels
Sometimes, the emissions caused by manufacturing an “eco-friendly” product makes it not so eco-friendly in the long run, but this is not the case for solar panels. The benefits of solar greatly outweigh any environmental cost. While the manufacturing of solar panels has a carbon footprint, it is relatively small compared to the carbon footprint of other energy sources, such as natural gas or oil extraction.
Quantifying the carbon footprint of solar panel manufacturing isn’t easy. There are a lot of moving parts, and production requirements for different types of solar panels can vary. On top of that, solar technology is still relatively new (compared to the world’s long history of fossil fuel extraction), so access to research about it is limited. That being said, we can look at some averages.
The general consensus is that due to the carbon emitted while manufacturing, during their first few years of use, solar panels produce around 50g (0.11lbs) of carbon per kilowatt-hour (kWh). The most significant contributor to solar manufacturing’s carbon footprint is producing the silicone used in the panels. Additionally, the mining, transportation, and melding of the metals used in solar panel manufacturing also increase its carbon footprint. The average American household with solar has around 20-25 solar panels. The carbon footprint of its manufacturing is not zero, but the carbon produced in manufacturing these panels is offset within the first 2-3 years of use. After the manufacturing of your panels, maintenance produces no carbon emissions, making their life-long carbon footprint miniscule compared to other energy sources.
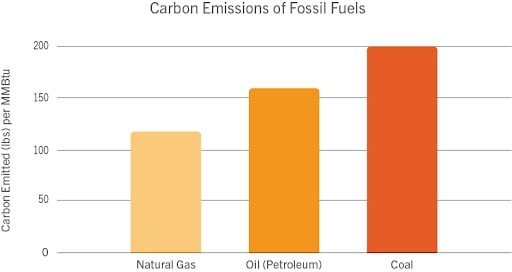 The emissions from manufacturing solar panels are significantly less than footprint of manufacturing or extracting other energy sources, such as natural gas, which produces around 117 lbs of carbon per million British thermal units (MMBtu), oil which produces around 160 lbs of carbon per MMBtu of oil, and coal mining which produces around 200 lbs of carbon per MMBtu of coal.
The emissions from manufacturing solar panels are significantly less than footprint of manufacturing or extracting other energy sources, such as natural gas, which produces around 117 lbs of carbon per million British thermal units (MMBtu), oil which produces around 160 lbs of carbon per MMBtu of oil, and coal mining which produces around 200 lbs of carbon per MMBtu of coal.
The amount of carbon emitted per MMBtu extracted varies depending on the energy source. However, the required amount of that energy source needed to power a home also varies. For example, the average American household that runs on natural gas uses around 95 MMBtu a year. Households that use oil require about 120 MMBtu of oil a year, and households that use coal require around 50 MMBtu of coal a year. This means that just the extraction of your energy source can emit 5-9 tons of carbon, depending on which energy source you use.
Previously, we thought that natural gas would be a legitimate way to lower our carbon footprints, but this was before we fully understood the carbon emitted during natural gas extraction. It’s true that burning natural gas to create electricity has a smaller carbon footprint than that of oil or coal, but due to the greenhouse gas emissions during natural gas extraction, it is still detrimental to our climate.
Solar Energy Production Has a Lower Carbon Footprint Than Burning Fossil Fuels
It’s no secret that solar panels don’t produce any carbon when they use the sun to produce energy, but let’s take a look at how that compares to other energy sources. Most traditional energy sources are burned in large quantities, which produces significant amounts of carbon dioxide emissions. We can break down the carbon footprints of different energy sources by looking at how much carbon is produced per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of energy used.
- Natural gas produces 0.91 lbs of carbon per kWh
- Oil (petroleum) produces 2.13 lbs of carbon per kWh
- Coal produces 2.23 lbs of carbon per kWh
The average American household consumes over 10,000 kWh of electricity per year. Depending on which fossil-fuel energy source you are using, that could account for 9,500 – 23,000 lbs of carbon per year; that’s 5-12 tons of carbon. The average American carbon footprint is 16 tons of carbon per year. Given that average, household energy consumption can make up a huge percentage of your carbon footprint.
Solar energy produces 0 lbs of carbon per kWh, which means the average American household can cut their carbon footprint down significantly just by swapping to solar energy. On top of that, if your solar system produces more electricity than you need, you can sell that extra electricity back to the grid via net metering to earn money while lowering your carbon footprint. Not only is solar great for reducing your footprint and emissions, but it is entirely renewable. The more we use fossil fuels, the less there is, and fossil fuels take millions of years to replenish. Solar energy is different because using it to produce electricity does not decrease the total amount of solar energy that is available to us. This is what makes it renewable and sustainable.
Solar Panel Disposal Isn’t Perfect, But It’s Getting There
Disposing of solar panels contributes to their carbon footprint, though the carbon footprint of their disposal still pales in comparison to the carbon footprint of traditional fossil fuels. The life expectancy of solar panels is at least 25 years, with many panels still functioning for 30-40 years, which means disposal happens infrequently.
If a solar panel does need to be disposed of, it is mostly recyclable. The majority of a solar panel is made of glass, which is 95% reusable. The panel’s aluminum frames can also be recycled. Panels only have a small amount of plastic, and the majority of this plastic can also be reused. Not only does this keep their carbon footprint low, but it reduces the need for raw materials for future panels or other products, which lowers the carbon footprint of future panels as well.
Most solar panels can be recycled at general-purpose glass recycling facilities. These locations will utilize the glass and sometimes the metal that can be reused. Some solar manufacturers are running programs to make the recycling of their products easier. Manufacturers like SunPower and Maxeon are some of the most prominent examples, and we hope to see other manufacturers follow their lead in the future.
It is important to keep in mind that solar energy is still a fairly new technology. Because solar panels have a long lifespan, there are not that many that have needed to be disposed of yet. It will be a growing priority to ensure that we have systems that allow us to recycle as many decommissioned solar panels as possible to ensure that their parts don’t end up in landfills. As time goes on, this disposal process will become more efficient and effective.
Go Solar To Reduce Your Carbon Footprint
Ultimately, the carbon footprint of solar panels is 20 times less than that of other energy sources. On top of this, the carbon footprint of solar panels only continues to decrease as we start to use solar and other renewable energy sources to produce them as well.
Because of its high energy production and low carbon footprint, going solar is one of the best choices that you can make to lower your carbon footprint. Reach out to Solaris Renewables to help you get started with solar energy and make strides in reducing your carbon footprint.
Lower Your Carbon Footprint With Solar
Fill out the form below to learn about the options for adding solar panels and other clean tech to your home to lower your carbon footprint.